Showing 37–45 of 1908 results
-
Acidum Oxalicum
Sorrel Acid
Although certain oxalates are constant constituents of vegetable food and of the human body, the acid itself is a violent poison when taken internally, producing gastro-enteritis, motor paralysis, collapse, stupor and death. Influences the spinal cord, and produces motor paralysis. Pains very violent, in spots (Kali bich) worse, motion, and thinking of them. Periodical remissions. Spasmodic symptoms of throat and chest. Rheumatism of left side. Neurasthenia. Tuberculosis.
-
Acidum phosphoricum
Phosphoric Acid
The common acid “debility” is very marked in this remedy, producing a nervous exhaustion. Mental debility first; later physical. A congenial soil for the action of Phos acid is found in young people who grow rapidly, and who are overtaxed, mentally or physically. Whenever the system has been exposed to the ravages of acute disease, excesses, grief, loss of vital fluids, we obtain conditions calling for it. Pyrosis, flatulence, diarrhœa, diabetes, rhachitis and periosteal inflammation. Neurosis in stump, after amputation. Hæmorrhages in typhoid. Useful in relieving pain of cancer.
-
Acidum picricum
Picric Acid-Trinitrophenol
Causes degeneration of the spinal cord, with paralysis. Brainfag and sexual excitement. Acts upon the generative organs probably through the lumbar centers of the spinal cord; prostration, weakness and pain of back, pins and needle sensation in extremities. Neurasthenia (Oxal ac). Muscular debility. Heavy tired feeling. Myelitis with spasms and prostration. Writer’s palsy. Progressive, pernicious anæmia. Uræmia with complete anuria. A one per cent solution applied on lint, is the best application for burns until granulations begin to form. Sallow complexion. -
Acidum salicylicum
Salicylic Acid
The symptoms point to its use in rheumatism, dyspepsia, and Meniere’s disease. Prostration after influenza; also tinnitus aurium and deafness. Hæmaturia.
-
Acidum sarcolacticum
(SARCOLACTIC ACID)
Is apparently formed in muscle tissue during the stage of muscle exhaustion. Differs from ordinary Lactic acid in its relation to polarized light. It represents a much broader and more profoundly acting drug and its pathogenesis is quite dissimilar from the normal acid. Proved by Wm. B. Griggs, M. D, who found it of great value in the most violent form ofEpidemic influenza, especially with violent and retching and greatest prostration, when Arsenic had failed. Spinal neurasthenia, muscular weakness, dyspnœa with myocardial weakness.
-
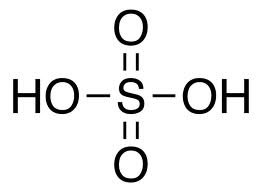
Acidum sulphuricum
Sulphuric Acid
The “debility” common to acids shows itself here, especially in the digestive tract, giving a very relaxed feeling in the stomach, with craving for stimulants. Tremor and weakness; everything must be done in a hurry. Hot flushes, followed by perspiration, with trembling. Tendency to gangrene following mechanical injuries. Writer’s cramp. Lead poisoning. Gastralgia and hypochlorrhydria. Purpura hæmorrhagia.
-
Acidum sulphurosum
Sulphurous Acid; H2 S O3
Sulphurous acid, (tonsillitis (as a spray), acne rosacea, ulcerative stomatitis, pityriasis versicolor).
-
Acidum tannicum
Tannin – Digallic Acid
(TANNIC ACID)Mostly used locally against excessive secretion of mucous membranes, to contract tissue and check hæmorrhage. In Osmidrosis, corrects fetor of the perspiration. Obstinate nervous coughs. Hæmaturia. Obstinate constipation. Pain in abdomen, sensitive to pressure. Intestines can be felt like cylindrical enlargements. One-half per cent solution.
-
Acidum tartaricum
Tartaric Acid
Found in grapes, pineapple, sorrel and other fruits. It is an antiscorbutic antiseptic, stimulating the mucous and salivary secretions.